Initial Outcome of Intravitreal Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (Anti-Vegf) at National Eye Centre (NEC), Kaduna
Vitreo-Retina
Abstract
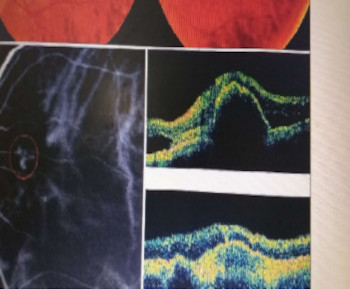
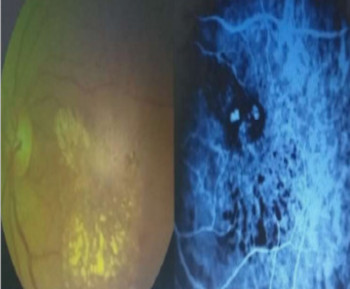
Introduction: The advent of intravitreal anti vascular endothelial growth factors has changed the course of various retinal diseases. Common indications include neovascular age-related macular degeneration (ARMD), diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusions (RVO), and retinopathy of prematurity.1-3Commonly used anti VEGFs include Bevacizumab (Avastin)R , Ranibizumab (Lucentis)R and most recently Aflibercept (Eylea)R . 4The aim of the study was to determine the indications and preliminary outcome (functional and structural) of intravitreal Anti – VEGF at National Eye Centre, Kaduna.
Methods: A retrospective review of patients who received intravitreal anti – VEGF for various retinal conditions from June 2013 – 2016.Patient’s biodata, diagnosis, co-morbid factor, type of Anti - VEGF, pre and post injection visual acuity, pre and post injection central foveal thickness (CFT). Patients were counselled and informed consent obtained. The eye prepared in the clinic and strict asepsis in theatre under topical anaesthesia (Tetracain by Alcon). A caliper was used at 4mm and 3.5mm from the limbus for phakic and psuedophakic eyes, respectively. Ranibizumab (0.5mg) and bevacizumab (1.25mg) were given in 0.1ml 30 or 32-gauge needle. Tamponade was achieved using sterile cotton buds at the injection site and eye padded. After an hour, the visual acuity and intraocular pressure (IOP) were measured and managed accordingly. Topical antibiotics and NSAIDs were given. Advised to come back when pain or reduced vision was noticed.
References
Okoye O, Okonkwo O, Oderinlo O, Hassan K. Bilateral concomitant intravitreal anti vascular endothelial growth factor injection: Experience in a Nigerian tertiary private eye care facility. Niger J. 2016.
Oluleye T S, Babalola Y. Indications for intravitreal bevacizumab in Ibadan, subSaharan Africa. Open Ophthalmol J. 2014; 8:87-90.
Al-Hinai A. Experience of intravitreal injections in a tertiary Hospital in Oman. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2015.
Saeed MU, Gkaragkani E, Ali K. Emerging roles for antiangiogenesis factors in management of ocular disease. Clinical Ophthalmology 2013:7; 533–543.
Grisanti S, Ziemssen F. Bevacizumab: Offlabel use in Ophthalmology. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2007 Nov-Dec; 55(6): 417– 420.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Transactions of the Ophthalmological Society of Nigeria

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.