Ocular Superglue Injury
Abstract
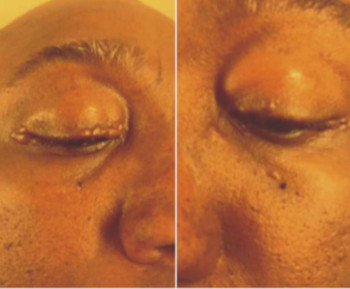
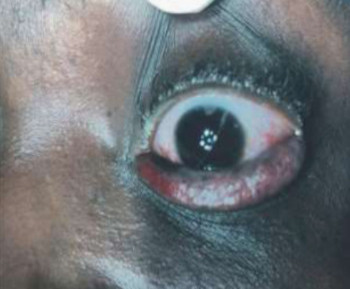
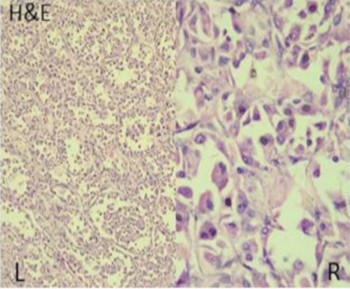
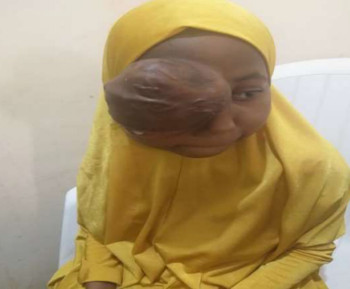
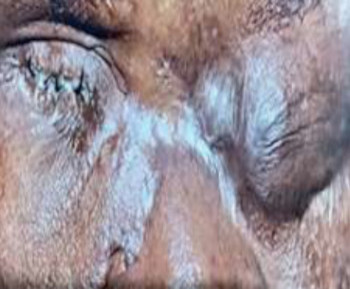
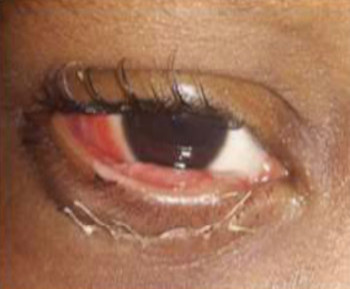
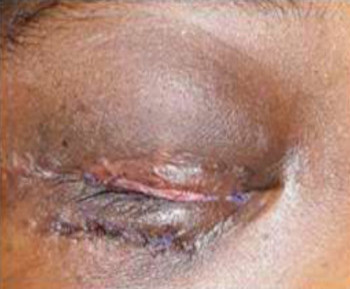
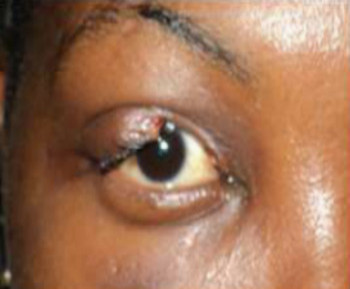
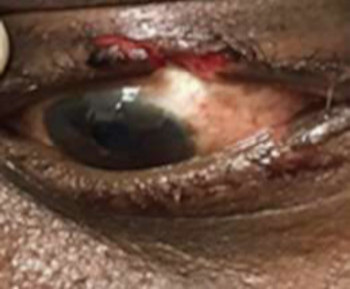
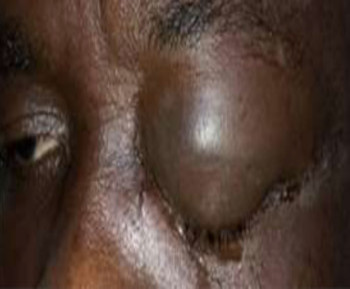
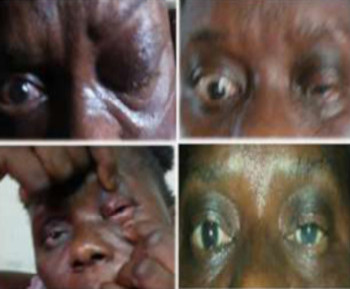
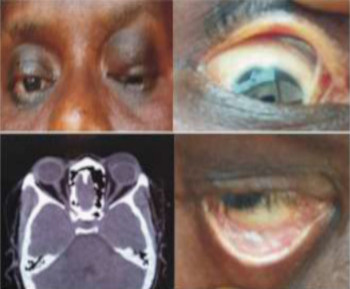
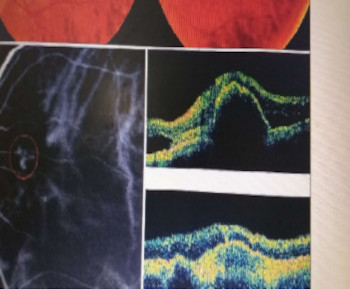
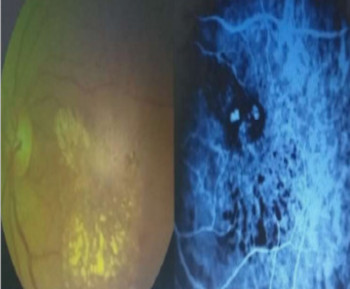
Eye care and prevention of trauma are crucial to the specialized function of the eye.1 Cyanoacrylate is the active component of Superglue.2 It has various uses, from industry to surgery.3,4 Its widespread availability and re-package style have also increased its presence in homes.4 Commercially available cyanoacrylate appeared in 1958, and in the 1980s, ophthalmic ointment-style packs such as Do-It-Yourself (DIY) and acrylic nail kits became available.5 It is however, toxic and use of gloves, glasses and mask are recommended.6 Scenarios of injury include poorly sighted individuals who mis-identify prescribed treatment, well sighted persons who carelessly introduce it into the eyes, children at unsupervised play and more recently, assault. 5,7-9Commercial cyanoacrylate is more toxic than the formulation used in medicine.10 Chemically, cyanoacrylate is a monomer formed from condensation of formaldehyde and cyanoacetate, forming a solid bond in less than 2 minutes, in dry conditions.11 Ocular injuries from cyanoacrylate mainly involve the external eye. Only dry surfaces, e.g. tarsal margin adhere together.8 On instillation, spontaneous blinking forces glue onto lid margins and lashes, with resultant adhesion. There is stinging or burning pain upon instillation, with loss of vision and resultant psychological distress. Eyelid skin excoriation, lash adhesion, lash loss, conjunctivitis, corneal abrasions with punctate erosions occur.8,12 There is however, no significant mechanical, chemical, thermal or toxic injury to ocular tissue.3 Primary treatment is reversal of acquired tarsorrhaphy, copious irrigation and use of wet patch.12 The tarsorrhaphy spontaneously resolves in about a week. However, amblyopia risk in children and the distress for even adults may require early intervention.8Secondary treatment includes care of ocular injuries along standard protocol; with appropriate treatment of corneal abrasion. Prognosis for visual recovery is excellent.5 Preventive measures include change in package style, using distinct colour and bold warning, simple modifications to opening caps, similar to child-proof safety mechanisms on toxic products.8,13. These are aimed against accidental instillation. This case report demonstrates this peculiar type of injury; with early surgical intervention and initial conservative measures producing a satisfactory visual outcome.
References
Mowatt L. Epidemiology of pediatric ocular trauma admissions. SurvOphthalmol. 2014; 59(4): 480
Vote B, Elder M. Cyanoacrylate glue for corneal perforations: a description of a surgical technique and a review of the literature. Clin Experiment Opthalmol 2000; 28: 437-442
Upender W, Rana A, Abdullah A. Cyanoacrylate-induced pseud-tarsorrhaphy of the eye. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2009 Jan-Apr;2(1):
-40
Margo C. Trobe J. Tarsorrhaphy from accidental instillation of cyanoacrylate adhesive in the eye. JAMA. 1982;247:660-661
Imran H, Patel C. A sticky sight: cyanoacrylate ‘superglue’ injuries of the eye. BMJ case Rep.2010;bcr11.2009.2435
Reddy S. Superglue injuries of the eye. Int J Ophthalmol. 2012;5(5):634-637
Desai S, Teggihalli B, Bhola R. Superglue mistaken for eye drops. Arch. Dis Child 2005; 90: 1193
McLean C. Ocular superglue injury. J. AccidEmerg Med 1997; 14:40-41
Mansouri M, Mirshashi A, Hosseini. Domestic ocular injuries: a case series. Eur J. Ophthalmol 2007; 17(4):654-659
Spencer T, Clark B. Self-inflicted superglue injuries. Med J Aust 2004; 181: 341
Deans B. Krenzelok E. Cyanoacrylates and corneal abrasion. Clin Toxicol. 1989; 27: 169-72
Good A, McCabe S. Superglue accidents and the eye-causes and prevention. Br J Ophthalmol 1994; 78: 802.
Tabatabari S, Modanloo S, Ghiyasvand A et al. Epidemiological aspects of ocular superglue injuries. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016;9(2):278-281
Cookey S, Chukwuka I, Sibeudu O. Rare chemical injuries: a case of ocular superglue instillation in Port-Harcourt. Int Med Case Rep J. 2018; 11: 209-212
Mandal A, Imram D, Erdmann M. Inadvertent application of superglue as eye ointment. Ir Med J. 2003; 96(10): 310-311