Pattern of Presentation of Pseudoexfoliation Deposits on the Lens Capsule in a Tertiary Eye Hospital in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Abstract
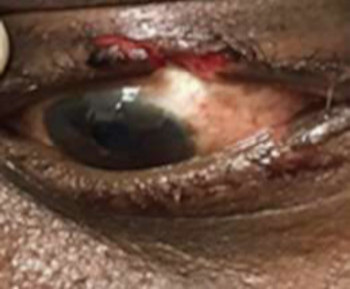
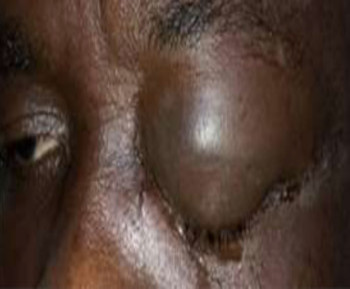
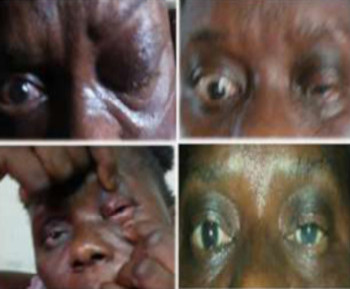
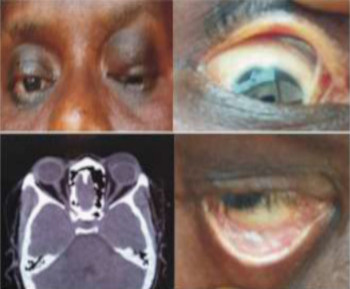
Pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PES) is an age-related systemic microfibrillopathy, caused by progressive accumulation and gradual deposition of extracellular grey and white material over ocular tissues.[1] This deposits are seen more commonly in the anterior segment of the eye, mainly the anterior lens capsule and iris.[2] PES can cause chronic open-angle glaucoma, angle closure glaucoma, lens subluxation and blood aqueous barrier impairment.[2] This study aims to provide data on the common pattern of presentation of pseudoexfoliation (PXF)deposits of the lens capsule in patients with PES and Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma (PEG) among the Bangladesh population.
References
Ritch, R., Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U. Exfoliation syndrome. Survey of Ophthalmology2001; 45 (4):265–315.
Naumann, G.O., Schlotzer-Schrehardt, U. and Kuchle, M. Pseudoexfoliation syndrome for the comprehensive ophthalmologist. Intraocular and systemic manifestations. Ophthalmology 1998; 105:951–968.
Brooks, A.M. and Gillies, W.E. The presentation and prognosis of glaucoma in pseudoexfoliaion of the lens capsule. Ophthalmology 1988; 95 (2):271-6.
Yildirim, N., Yasar, E., Gursory, H. and Colak. E. Prevalence of pseudoexfoliation syndrome and its association with ocular and systemic diseases in Eskisehir, Turkey.Int J Opthalmol. 2017; 10 (1):128-134.
Layden, W. E. and Shaffer R N. Exfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974; 78(5):835–841
Sunde, O. A. On the so-called senile exfoliation of the anterior lens capsule; a clinical and anatomical study. Acta OphththalmolSuppl 1956;(Suppl 45) :1-85
Rao, A. and Padhy D. Pattern of pseudoexfoliation deposits on the lens and their clinical correlation—clinical study and review of literature, PLoS 2014; 5:9(12)
Summanen, P. and Tönjum, A. M. Exfoliation syndrome among Saudis. Acta Ophthalmologica. 1988; 184 (supplement):107–111.
Ritch, R. “Exfoliation syndrome: the most common identifiable cause of open-angle glaucoma,” Journal of Glaucoma. 1994; 3(2):176-178