Management of Cystic Lid Masses with Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate (STS) Sclerosant
Abstract
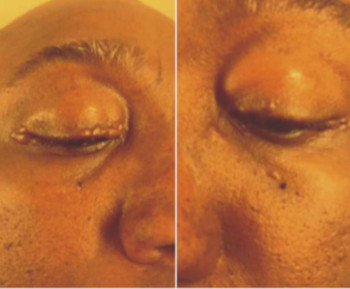
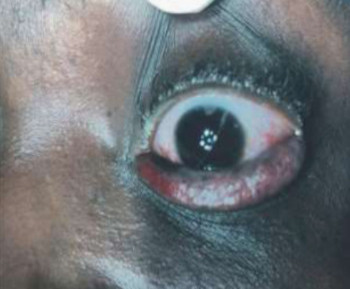
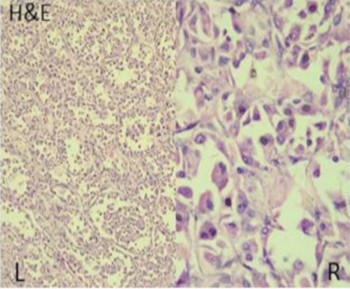
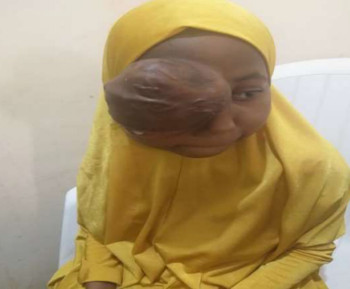
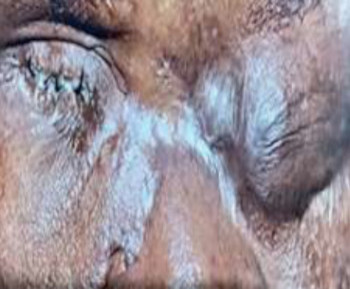
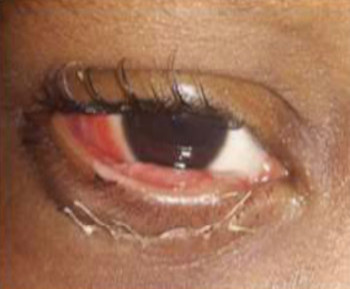
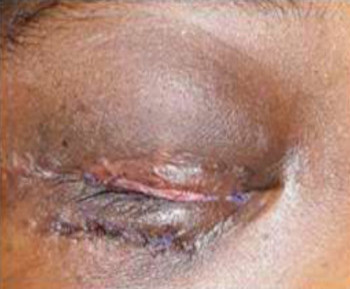
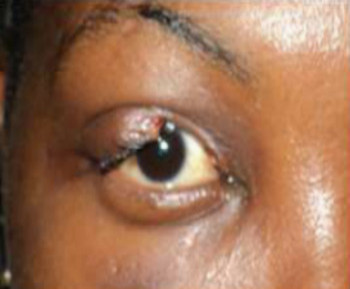
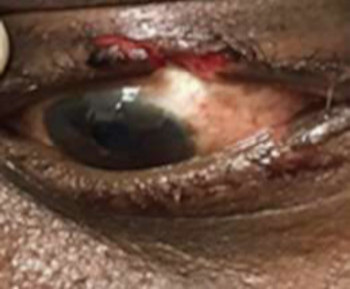
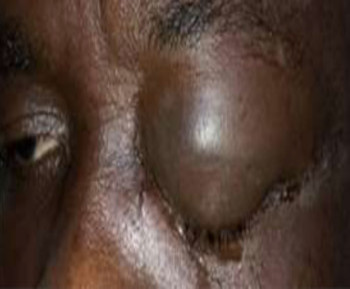
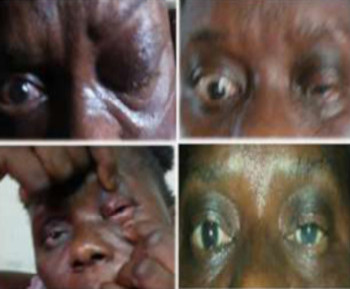
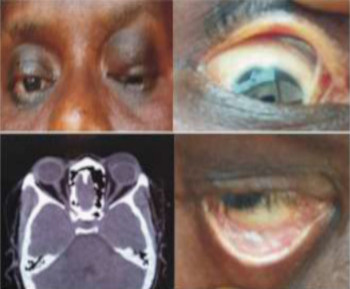
A dermoid cyst is a congenital choristoma of the orbit. It consists of keratinized epithelium and adnexal structures such as hair follicles, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands.1 The mainstay of treatment is surgery but if the cyst ruptures during surgery, a lipogranulomatous inflammatory reaction may occur. This necessitates the use of sclerosants which are less invasive. Here in we report the use of sodium tetradecyl sulfate (STS) in the management of cyst of Moll and dermoid cyst.
References
Sherman RP, Rootman J, Lapointe JS. Orbital dermoids: clinical presentation and management. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984; 68: 642-652.
Shields JA, Kaden IH, Eagle RC, Shields CL. Orbital dermoid cysts: clinicopathologiccorrelations, classification, and management. OphthalPlastReconstr Surg. 1997; 13:265–276.
Castillo BV, Jr, Kaufman L. Pediatric tumors of the eye and orbit. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2003; 50:149–172.
Imtiaz AC.Management of Deep Orbital Dermoid Cysts.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2008 Jan-Mar; 15(1): 43–45.
Basic Clinical and Science Course. Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 2013-14. Section 6: 343-344
Naik, Milind N., Jyoti Batra, Akshay G. Nair, Mohammad Javed Ali, Swathi Kaliki, and Dilip K. Mishra. “Foam Sclerotherapy for Periorbital Dermoid Cysts.” Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2014, 1.